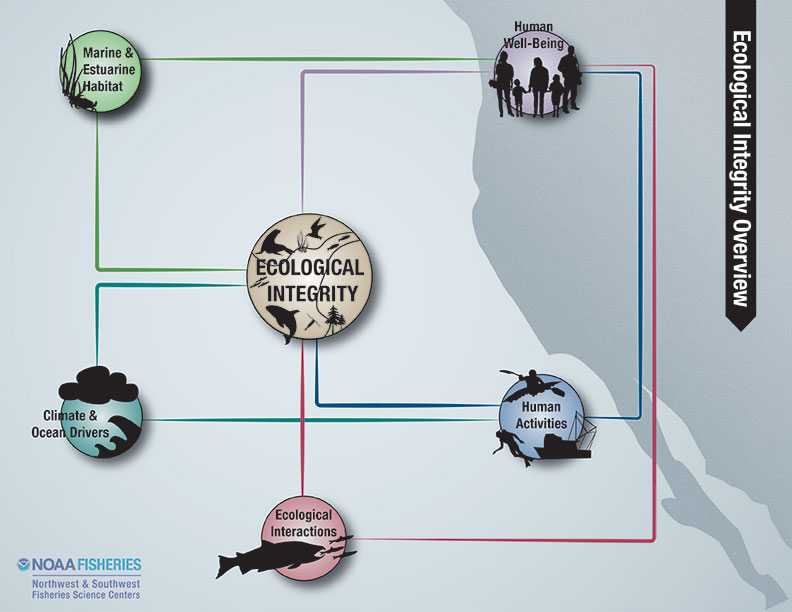
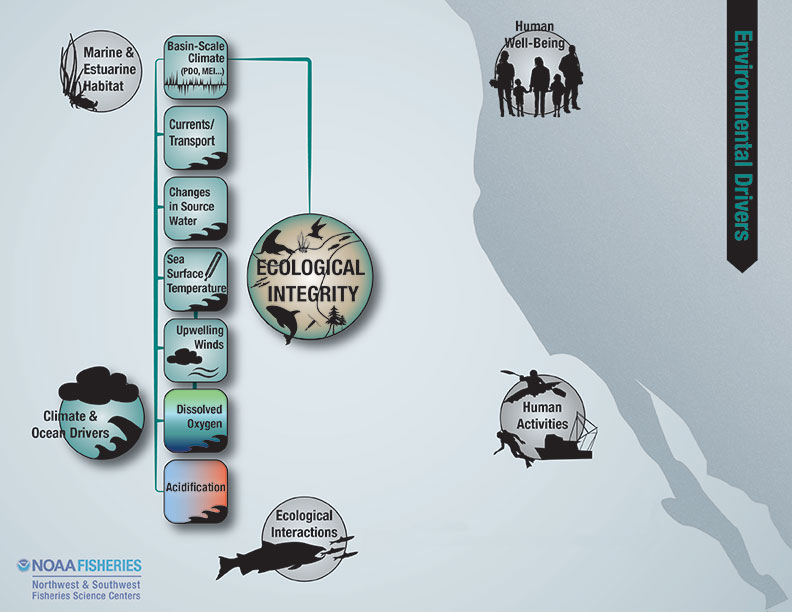
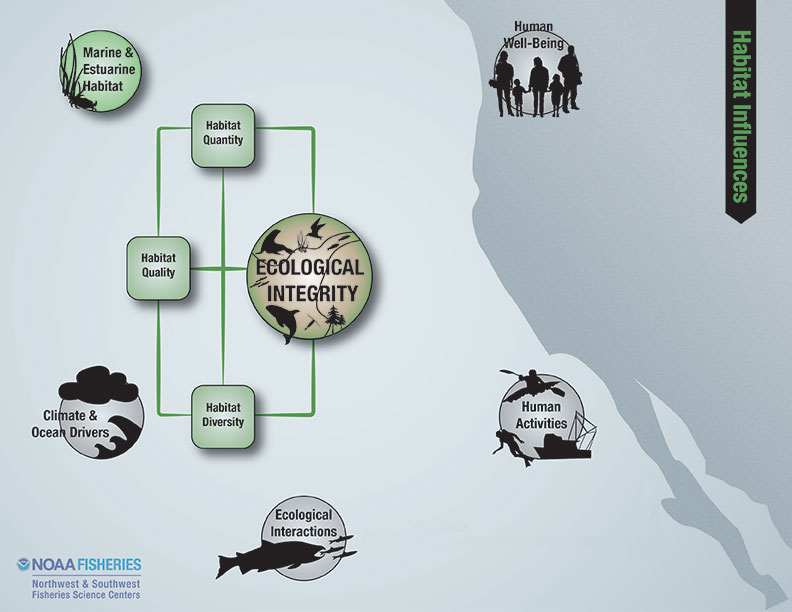
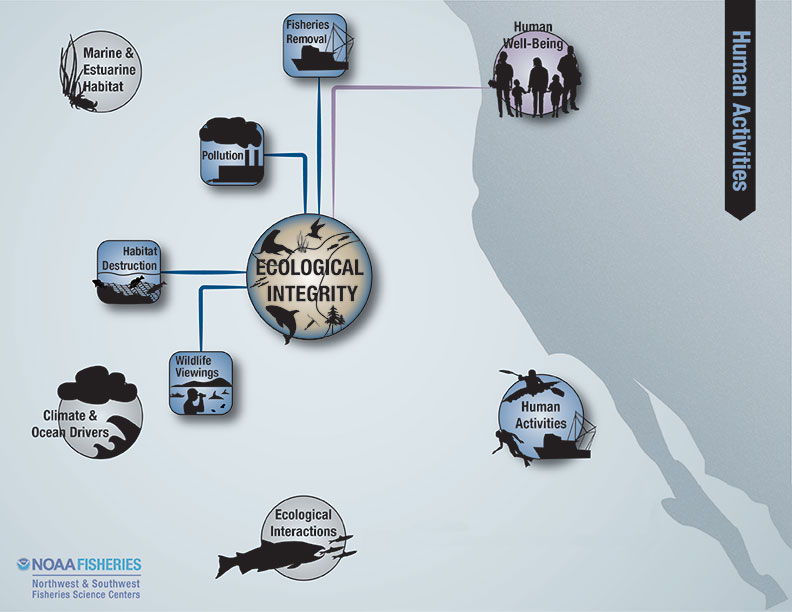
Ecological integrity is intended to measure the species composition, diversity, and functional organization of the ecosystem.
The indicators reported in this section are designed to be integrative, community-based measures that draw information from across the taxonomic spectrum. Indicators specific to individual ecological components also provide information that can influence ecological integrity and are covered in other sections of this report.